Introduction To Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) have become a popular investment option for individuals and institutions seeking to diversify their portfolios and generate steady income streams. REITs allow investors to invest in a portfolio of properties, such as office buildings, apartments, shopping centers, and hotels, without directly owning physical real estate. In this article, we will delve into the world of REITs, exploring their history, types, benefits, and risks, as well as providing an overview of the current market trends.
History of REITs
The concept of REITs was first introduced in the United States in 1960, when Congress passed the Real Estate Investment Trust Act. The law allowed investors to pool their resources to invest in a diversified portfolio of properties, providing a way for individuals to participate in the real estate market without directly owning physical assets. Since then, REITs have grown in popularity, with the global REIT market now valued at over $3 trillion.
Types of REITs
There are several types of REITs, each with its own unique characteristics and investment strategies. The main types of REITs include:
- Equity REITs: These REITs invest in and own properties, generating income through rental income, property sales, and other related activities.
- Mortgage REITs: These REITs invest in mortgages and other debt securities, earning income through interest payments.
- Hybrid REITs: These REITs combine elements of equity and mortgage REITs, investing in both properties and debt securities.
- Specialized REITs: These REITs focus on specific types of properties, such as healthcare facilities, technology infrastructure, or timberlands.
Benefits of Investing in REITs
REITs offer several benefits to investors, including:
- Diversification: REITs provide a way to diversify a portfolio, reducing reliance on traditional assets such as stocks and bonds.
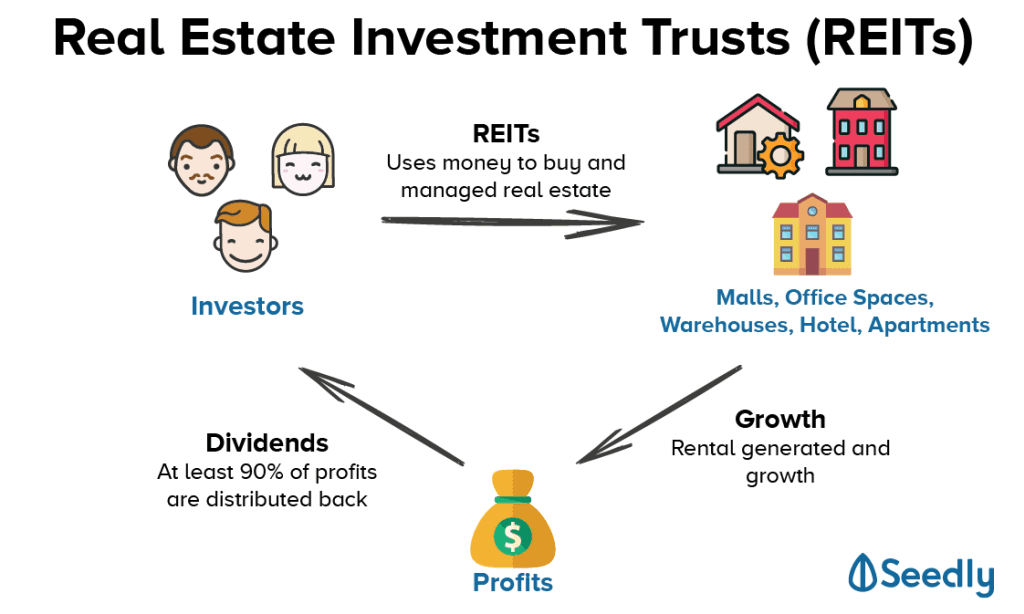
- Income generation: REITs are required to distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders, providing a steady stream of income.
- Professional management: REITs are managed by experienced professionals, allowing investors to tap into their expertise and resources.
- Liquidity: REITs are traded on major stock exchanges, providing investors with easy access to their investments.
Risks of Investing in REITs
While REITs offer several benefits, they also come with some risks, including:
- Market volatility: REITs are subject to market fluctuations, which can impact their value and income generation.
- Interest rate risk: Changes in interest rates can affect the value of REITs, particularly mortgage REITs.
- Property market risk: REITs are exposed to risks associated with the property market, such as changes in demand, supply, and regulations.
- Concentration risk: Investors who focus on a single REIT or sector may be exposed to concentration risk, which can increase their vulnerability to market fluctuations.
Current Market Trends
The REIT market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by strong demand for income-generating assets and a low-interest-rate environment. However, the market is not without its challenges, with some REITs facing headwinds from rising interest rates, increasing competition, and regulatory changes.
Some of the current trends in the REIT market include:
- Urbanization: Many REITs are focusing on urban areas, where demand for housing, office space, and other types of properties is high.
- Sustainability: Investors are increasingly looking for REITs that prioritize sustainability and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors.
- Technology: The use of technology, such as artificial intelligence and blockchain, is becoming more prevalent in the REIT industry, enabling greater efficiency and transparency.
FAQs
- What is the minimum investment required to invest in a REIT?
The minimum investment required to invest in a REIT varies, but many REITs have a minimum investment requirement of $1,000 to $5,000. - How do I invest in a REIT?
You can invest in a REIT through a brokerage account or by purchasing shares directly from the REIT. - What is the typical dividend yield for a REIT?
The typical dividend yield for a REIT ranges from 4% to 8%, depending on the type of REIT and market conditions. - Are REITs suitable for long-term investors?
Yes, REITs can be suitable for long-term investors, as they provide a steady stream of income and the potential for long-term capital appreciation. - How do I evaluate the performance of a REIT?
You can evaluate the performance of a REIT by reviewing its financial statements, such as its income statement and balance sheet, as well as its operating metrics, such as occupancy rates and rental income.
Conclusion
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) offer a unique opportunity for investors to participate in the real estate market without directly owning physical assets. With their diversified portfolio of properties, professional management, and steady stream of income, REITs can provide a attractive investment option for individuals and institutions seeking to generate returns and diversify their portfolios. While REITs come with some risks, such as market volatility and interest rate risk, they can be a valuable addition to a well-diversified investment portfolio. By understanding the benefits and risks of REITs, as well as the current market trends, investors can make informed decisions and capitalize on the opportunities presented by this asset class. Whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting out, REITs are definitely worth considering as part of your investment strategy.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Introduction to Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs). We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!










Post Comment